Innovation, Sustainability, Legacy

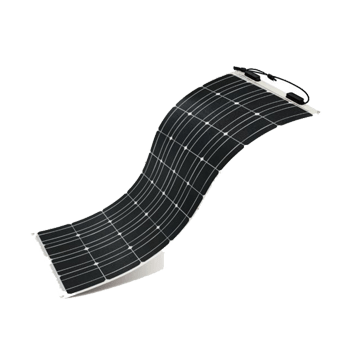
Solar energy begins with the sun.
Solar panels convert light from the sun, which is composed of particles of energy called “photons”, into electricity. The surface of the Solar panels absorb the photons that generate energy. This allows the electrons to be released into the electric field in the solar cells pulling these free electrons into a directional current. This process is known as Photovoltaic Effect.
© 2024 Sene Pte Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Website By Creative eWorld Pte Ltd.